[Solved] Determine the radius of gyration of the crosssectional area with... Course Hero
This equation computes the Radius of Gyration (RG) of a solid cylinder about the x c x c axis, the axis parallel to the x-axis and through the center of the solid cylinder. The Radius of Gyration about a given axis can be expressed in terms of the moment of inertia as: r 2 = I axis m r 2 = I axis m. This equation is computing specifically the.
Radius of Gyration 17 Engineering Mechanics Lab theory for helping made a particles Theory
The Radius of Gyration about a given axis can be expressed in terms of the moment of inertia as: r2 = Iaxis m. This equation is computing specifically the radius of gyration about the x-axis defined in the picture. Because of symmetry of the cylinder, the radius of gyration about the y-axis is the same for the radius of gyration about the point.
How to find Radius of Gyration Example Solved YouTube

The radius of gyration is defined as the distance from the axis of rotation to the point where the whole mass/area of a body is supposed to be concentrated which gives the same moment of inertia as that of the original shape. 2. The position of centroid (x̄, ȳ) is given by, x̄ = ∫x. dA ∫dA ∫ x. d A ∫ d A.
Radiusof Gyration Feigin Svergun Book
2.4: Radius of Gyration. Page ID. Jeremy Tatum. University of Victoria. The second moment of inertia of any body can be written in the form mk2 m k 2. Thus, for the rod, the disc (about an axis perpendicular to its plane), the triangle and the disc (about a diameter), k k has the values. l 3-√ = 0.866l l 3 = 0.866 l, a 2-√ = 0.707a a 2.
Engineering Mechanics C7L4 Radius of Gyration of an Area YouTube

Definition. The Radius of Gyration, denoted usually by 'k', is a measure that describes the distribution of a cross-sectional area of a column (or any structural member) around an axis. More precisely, it is the square root of the area moment of inertia divided by the cross-sectional area.
Definition Radius Of Gyration information online

RADIUS OF GYRATION. In terms of mass, the radius of gyration is a quantity in length for a rotating system, measuring the distance from a point P of a point mass of the same mass of the object of interest which would have the same moment of inertia I zz of the body. (1) Ipzz = mK2p. If the radius of gyration at the center of mass of the body.
The radius of gyration of a solid cylinder of mass M and radius R about its own axis is

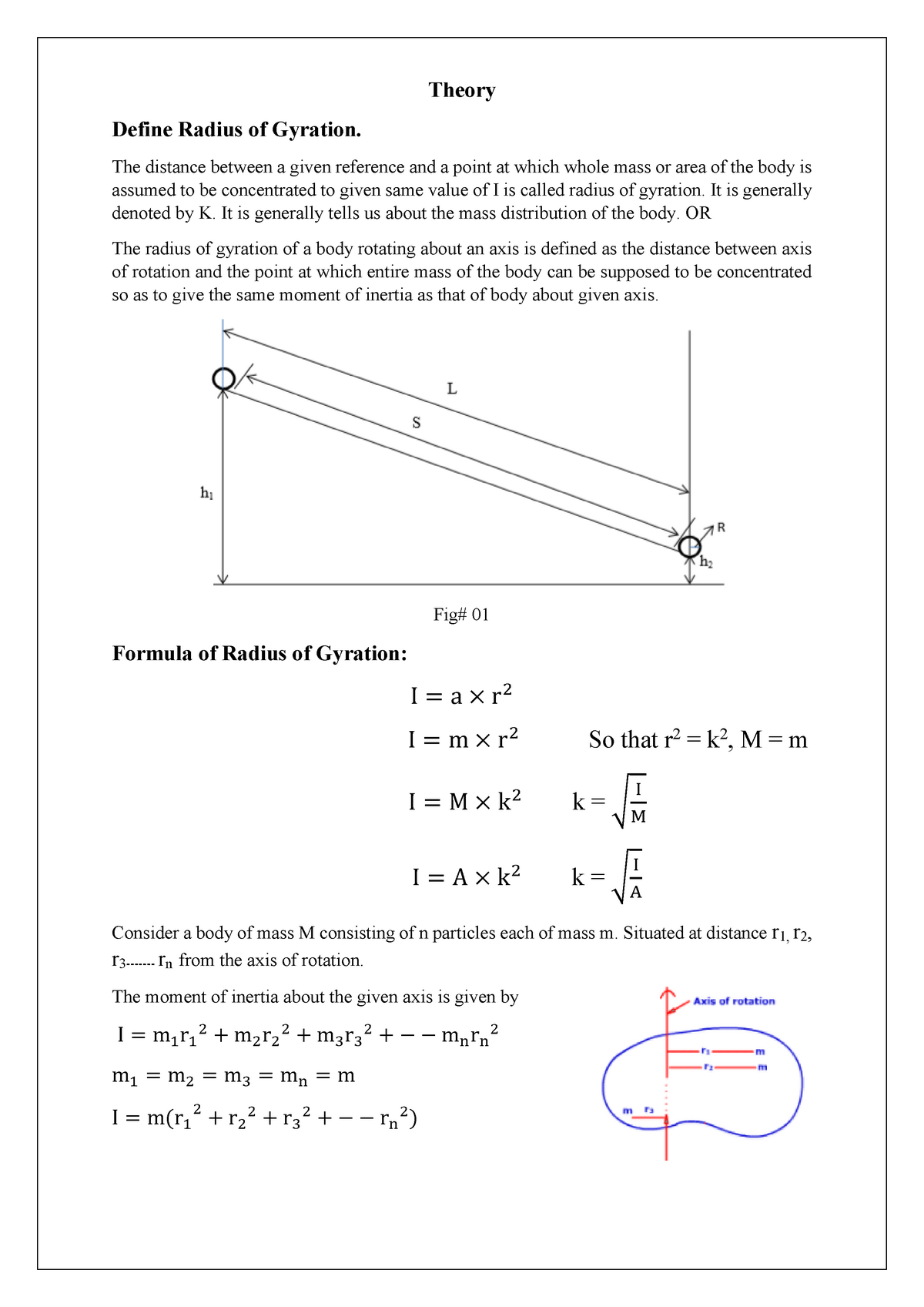
7.4.3 Radius of Gyration. A concept called the radius of gyration (k) converts a shape into a thin ring. This is used for particularly complex shapes. If a homework problem says 'the radius of gyration k = 15 cm', that means if the shape were a thin ring, it would have a radius of 15 cm.
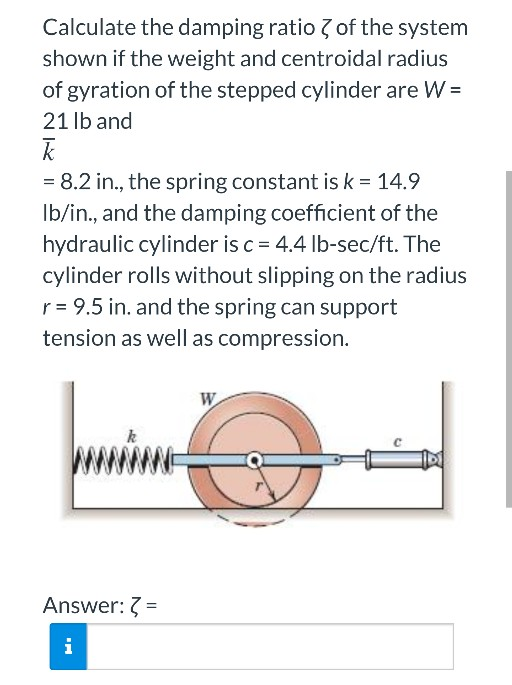
Solved Calculate the damping ratio of the system shown if
Radius of Gyration. Area. y. Related: Engineering Section Properties Common Shapes; Section Modulus Equations and Calculators; Section Properties Radius of Gyration Cases 1 - 10; Section Properties Radius of Gyration Cases 11 - 16; Section Properties Radius of Gyration Cases 23 - 27;
What is the Radius of Gyration? The StructEd

Mechanics: Here radius of gyration about an axis of rotation is calculated using mass moment of inertia and its formula is given by relation, k =√ I M (1) (1) k = I M This equation (1) is the radius of gyration formula for mass moment of inertia. here, M M is mass of the rotating object and I I is the moment of inertia about any axis of rotation.
The radius of gyration of a solid cylinder of mass M and radius R about its own axis is

Radius of Gyration. For a planar distribution of mass rotating about some axis in the plane of the mass, the radius of gyration is the distance from the axis that all mass can be concentrated to obtain the same mass moment of inertia. Thus, the radius of gyration is the ``equivalent distance'' of the mass from the axis of rotation. In this.
The radius of gyration of a solid cylinder of mass M and radius R about its own axis is

The formula for calculating the radius of gyration in the Radius of Gyration Calculator is as follows: Radius of Gyration (k) = sqrt (Moment of Inertia / Mass or Area) In this formula: Moment of Inertia: The moment of inertia represents the object's resistance to rotational motion and is calculated based on the mass or area distribution and.
Momento De Inercia Tubo EDUCA
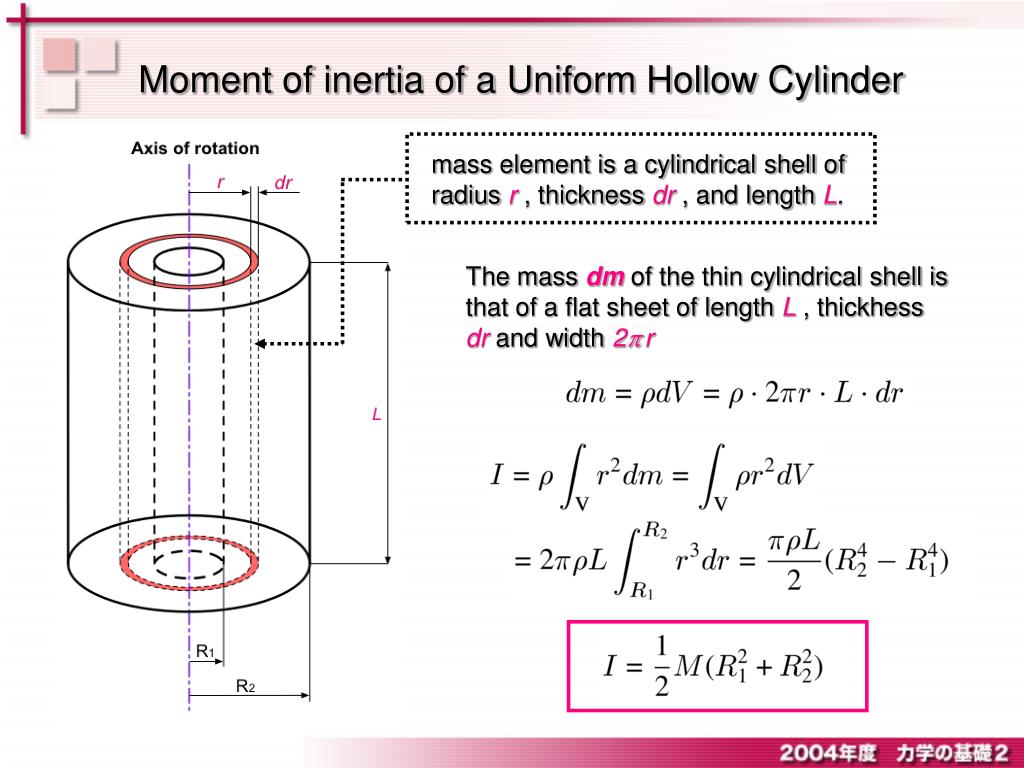
The unit of the radius of gyration is mm. By knowing the radius of gyration, one can find the moment of inertia of any complex body equation (1) without any hassle. Consider a body having an n number of particles each having a mass of m. Let the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation be given by r 1, r 2, r 3,…,r n. We know that the.
Engineering Mechanics Statics Theory Radius of Gyration YouTube

The radius of gyration of an equivalent freely jointed chain is given by < R g 2 = Nb 2 ∕ 6 = < R 2 > ∕ 6. That is, the radius of gyration is smaller than the root mean square end-end distance by a factor of . It is instructive to remember that the radius of gyration of a solid sphere is not equivalent to its physical radius. For a sphere.
The radius of gyration of a uniform disc about a line perpendicular to the disc equals its

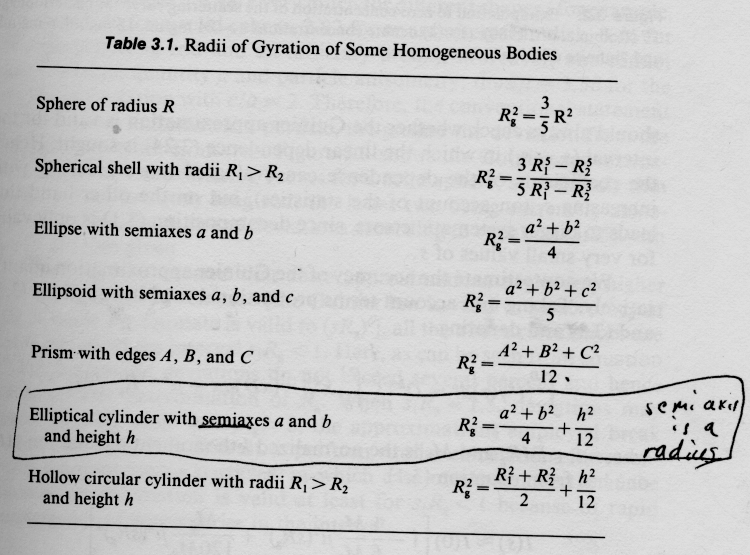
The Radius of Gyration kx of an Area (A) about an axis (x) is defined as: Radius Gynation can be expressed as:- RG = sqrt(9r^2 + 12 h^2)/6 Where:- RG = Radius Gynation r = Radius of the Cylinder h = Height of a cylinder
Radius of Gyration Formula YazminhasDillon

Radius of gyration (in polymer science)(, unit: nm or SI unit: m): For a macromolecule composed of mass elements, of masses , =1,2,…,, located at fixed distances from the centre of mass, the radius of gyration is the square-root of the mass average of over all mass elements, i.e., = (= / =) / Note: The mass elements are usually taken as the masses of the skeletal groups constituting the.
The radius of gyration of a solid cylinder of mass M and radius R about its own axis is

The radius of gyration with respect to the x x and y y axes and the origin are given by these formulas. kx = Ix A−−−√ ky = Iy A−−−√ ko = Jo A−−−√. (10.6.1) (10.6.1) k x = I x A k y = I y A k o = J o A. In engineering design, the radius of gyration is used to determine the stiffness of structural columns and estimate the.